Megaladata 7.3—A Major Release


New capabilities of working with data trees
The Tree to JSON component converts a hierarchical tree structure into a dataset where each row contains a JSON object. If the root node of the tree is an array, the component generates a separate output row for each element in that array. The node configuration wizard allows users to define root node processing logic, date and time conversion formats, and JSON naming conventions.
The JSON to Tree component converts JSON data into a hierarchical tree structure. It provides flexible parsing, with the option to create the tree automatically or manually. For easier management of large structures, you can load a tree pattern from an XSD schema or directly from a JSON file.
The new Tree Union component combines data from multiple input trees into a single output structure. It operates in one of two modes:
- Concatenate all trees: Consolidates root nodes from all active input ports into a single root array.
- Select the first active tree: Outputs data from the first input port that contains an active tree.
Note on Data Types: In Select the first active tree mode, the component checks all input ports for array definitions. If any connected input port has an array structure (even if currently inactive), the component forces the output into an array format. This ensures consistency when the node follows a Condition node where only one branch contains an active data tree.
The Tree Join component allows you to attach data from a secondary tree to a specific node within a main tree, creating an expanded hierarchical structure.
When configuring this component, you can attach the root of the secondary tree in one of two ways:
-
As a child node of a container in the main tree.
-
As a new element within an array in the main tree
New component: SQL Script
The new SQL Script component is designed to perform custom SQL requests in various DBMSs. It supports the execution of non-cursor-returning scripts and handles transactions. The component requires configuring a connection to a relevant database, similar to the Database import and export components. The component receives both tabular data and variables as input, and the output contains execution statuses and errors.
The node configuration wizard features an SQL editor with syntax highlighting and code completion. Input fields and variables can be used directly within your scripts as parameters or macro substitutions.
-
Advanced configuration: A separate wizard page allows you to configure additional settings, such as execution timeouts or error suppression.
-
Usage: This component integrates seamlessly into standard workflows. Common use cases include creating a new database table and immediately populating it, or executing a specific script for each row of input data.
-
Important: The SQL Script component has limitations related to executing scripts and transactions in different DBMSs
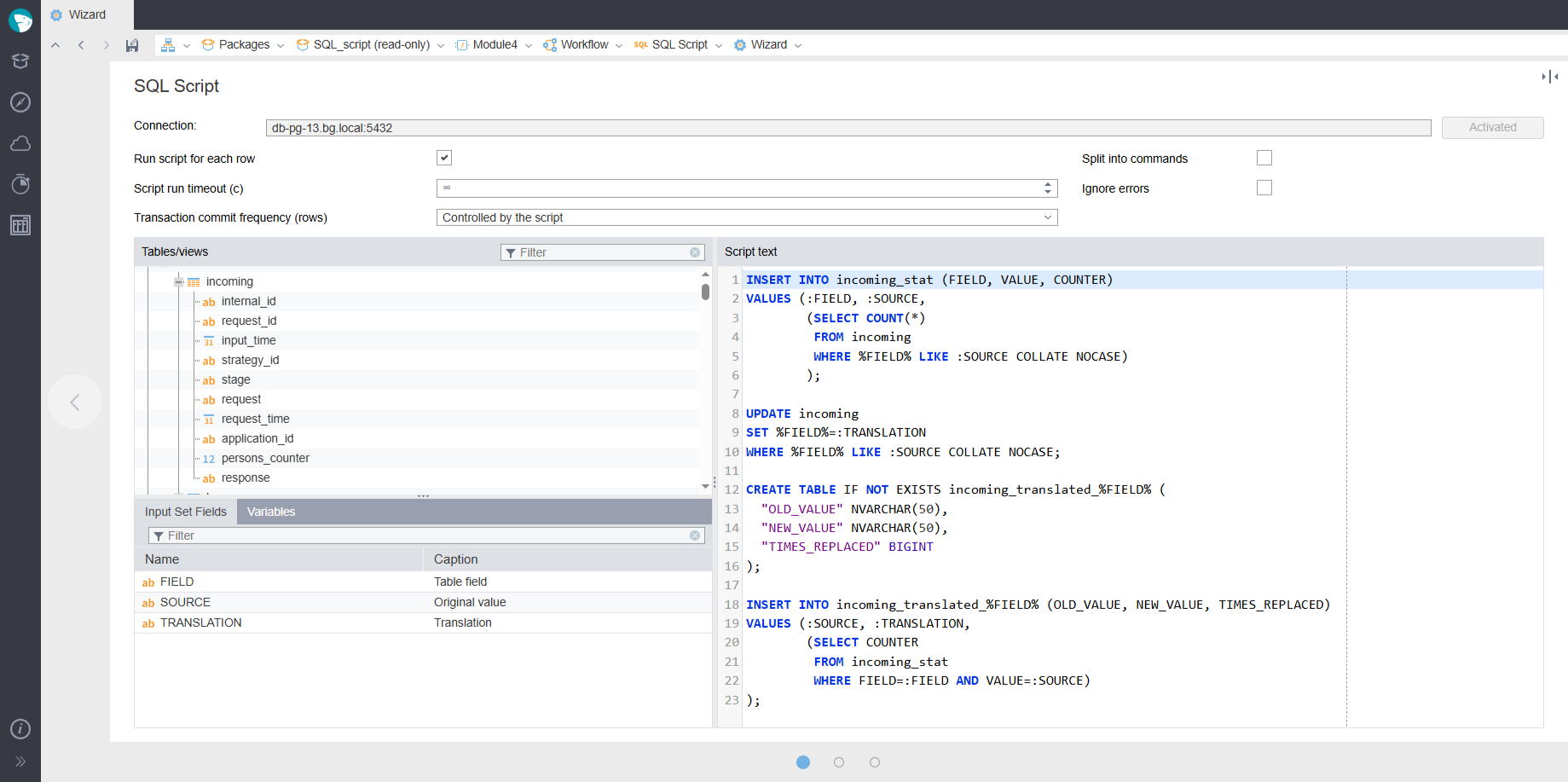
The SQL Script wizard
Row Filter redesigned
The Row Filter configuration wizard has been completely redesigned. The main setup window is now a table, where conditions are set in rows. To set a condition, select a field in the first column, an operator in the second, and a comparison value in the third. Complex conditions are created using multiple rows, connected with the AND operator by default. If you need to use the OR operator, set it explicitly between the rows using the context menu or the toolbar.
A similar wizard was introduced in the Table visualizer's filter and the Data Filter page of the Database import node.
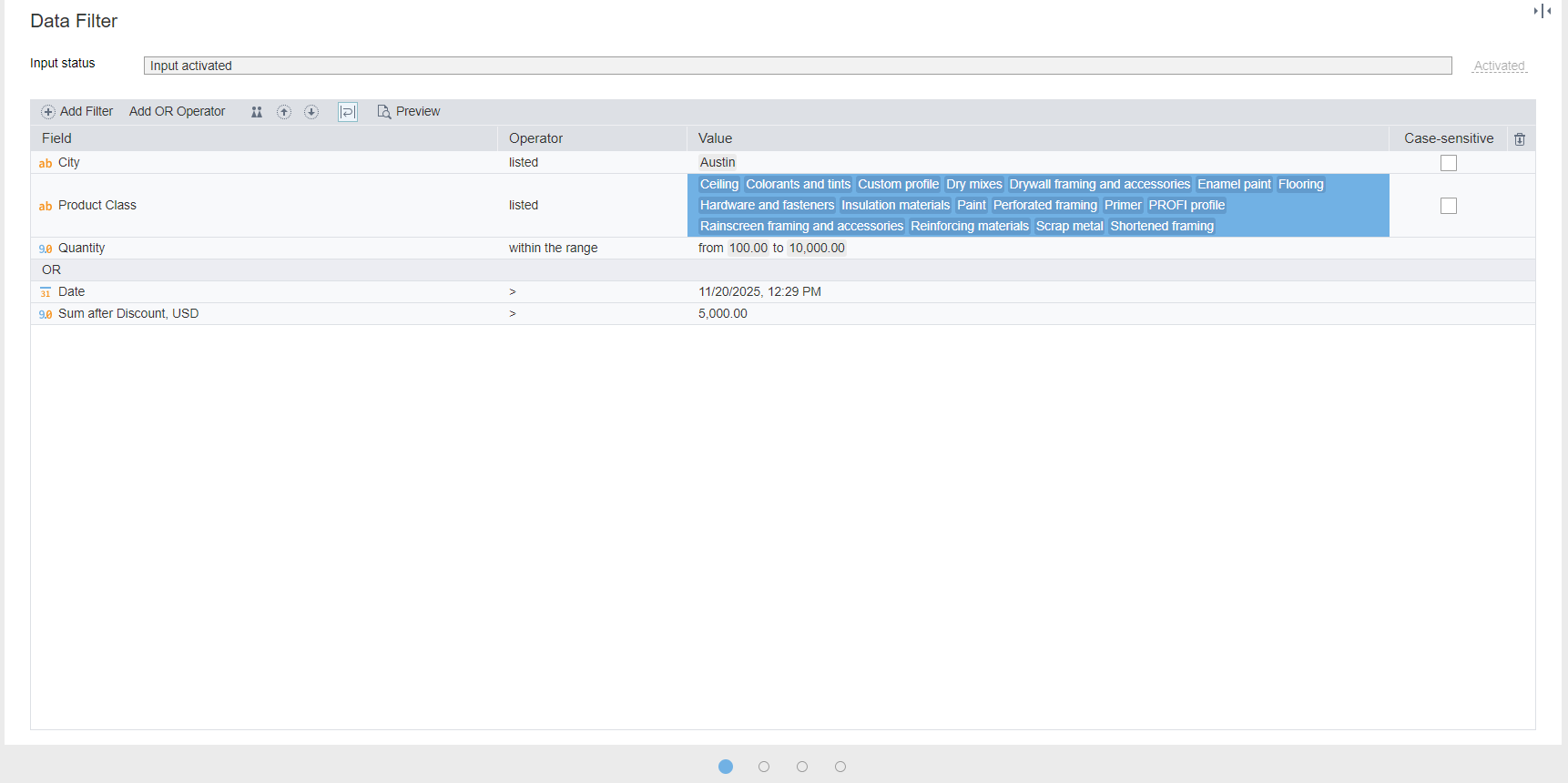
New Row Filter wizard
Changes to database-operating components
Connecting to a database without using a connection pool
When you configure a connection to the database, you can now opt out of using the connection pool by selecting Single session work mode. In this mode, the connection allows exclusive access to only one node at a time. When another node requests the session simultaneously, the error message Connection to DB is busy will be displayed.
Note: Single session work mode preserves the session state, allowing you to operate on temporary tables across several nodes sequentially.
When configuring the connection, along with the single session work mode, you can set a Session wait timeout (s).
With this setting, if a second node attempts to access the connection while it is busy, it will wait for the specified time. If the session does not finish within the timeout, the process ends with the 'Connection to DB is busy' error. The timeout ranges from 0 to 2073600 (24 days). You can also cancel the waiting process from the Processes pane.
Single session work mode specifics:
- Unsupported connections: Single session mode is unavailable for connections to MS Access, MS Excel, and other ODBC/Microsoft Office Access Engine connections.
Note: The option remains visible in the ODBC connection wizard because the system cannot identify the specific driver until the connection is active.
- Connection behavior: The connection appears in the Processes pane only once. If the connection is lost, the system does not reconnect automatically.
- SQLite behavior:
- Import: You cannot run multiple Database import nodes simultaneously. If a wait timeout is set, these nodes are queued and executed sequentially as the session becomes available.
- Export: While the system allows you to configure parallel export branches without error messages, the Database export nodes will technically be queued and executed sequentially based on the specified timeout.
New features for working with ClickHouse
Support for ClickHouse clusters has been implemented. In the ClickHouse connection config wizard, a new Cluster parameter is now available. You can select the target cluster from the drop-down list.
Note: For ClickHouse Cloud, this parameter is ignored and the list will be empty.
When a Cluster is specified, the Database export component modifies its execution logic as follows:
- The
CREATE TABLErequest creates two tables:- A data table (suffix
_data) usingENGINE = ReplicatedMergeTreefor automatic replication in the cluster. If you executeINSERT INTOon this table, data is written only to the connected server. - A distributed table. If you execute
INSERT INTOon this table, data is evenly distributed across the cluster tables.
- A data table (suffix
- The
DROP TABLErequest is prepared using theON CLUSTER {cluster}clause. If a distributed table is specified, the data is also deleted from the underlying source tables. - The
DELETE FROMrequest is converted to aTRUNCATE TABLErequest. - The
ALTER TABLE ... DELETE FROMmutation (used for deletion by keys) and theTRUNCATE TABLErequest are both executed usingON CLUSTER {cluster}. If a distributed table is targeted, the data is deleted from the underlying local tables. However, if the distributed table belongs to a cluster other than the one specified in the Cluster parameter, the execution will end with an error.
Features of importing from a database when working in cluster mode:
- If you import a distributed table
{db}.{table}, the data is concatenated from all cluster tables specified in the distributed engine arguments:Distributed(cluster, database, table[, sharding_key[, policy_name]]) - If you import from the data tables
{db}.{table}_data, the data is imported only from the server to which you're connected.
New settings in the ClickHouse connection wizard:
- Network send timeout (s): Sets the maximum time allowed for sending package data to the server. If the data cannot be written within this time, the connection is terminated.
- Default value (in seconds):
120 - Range:
[0 to 2073600](up to 24 days).0indicates an infinite timeout.
- Default value (in seconds):
- Network receive timeout (s): Sets the maximum time allowed for reading incoming package data. If no data is received within this time, the connection is terminated.
- Default value (in seconds):
120 - Range:
[0 to 2073600]
- Default value (in seconds):
Changes in working with MS SQL Server
New settings added to the MS SQL connection allow you to establish a secure connection to MS SQL Server even if encryption is not explicitly configured on the server side. The default encryption settings are as follows:
- Encrypt the protocol: The default value is
False. - Do not check server certificate: The ceritificate is verified (the value is
False). The setting is not displayed in the connection wizard if the Always verify all certificates option is enabled in the security settings (in the Administration section).
-
Important:
- The Encrypt the protocol and Do not check server certificate settings may be overridden by global OLEDB driver settings in the Windows registry or the specific driver version.
- Setting Encrypt the protocol to
Falsedoes not guarantee a non-encrypted connection, as encryption might be enforced by the server or the Windows registry. - MS SQL OLEDB 18 (and earlier): These drivers never check the server certificate, even if the protocol is encrypted.
- MS SQL OLEDB 19: This driver skips the certificate check only if both Trust Server Certificate is disabled in the registry and Encrypt the protocol is set to
Falsein the application. In all other cases, the certificate is verified. - Linux: When connecting without a native client, if Encrypt the protocol is enabled (even if the server doesn't require it), the certificate is checked. Note that self-signed certificates will fail this check.
When working in Megaladata on Linux, ODBC client connections are supported when the Do not use DBMS client option is disabled. The system uses MSODBCSQL (priority) or FreeTDS.
Note: On Linux, new MS SQL connections use the ODBC client by default (the Do not use DBMS client option is disabled). This is the intended method for interacting with MS SQL on Linux due to the superior stability of ODBC drivers and comprehensive protocol support
Important: When opening packages created in earlier Megaladata versions, the Do not use DBMS client option is reset to its default (i.e., disabled). This means MS SQL connections will stop working if the system lacks the appropriate ODBC driver (MSODBCSQL or FreeTDS). Additionally, when moving a package from Windows to Linux, the connection will automatically use the ODBC driver.
Available settings:
- If the environment variable
MEGALADATA_MSSQL_ODBC_ONLYis set totrueor1, the connection to MS SQL is performed through ODBC only. - Using the environment variable
MEGALADATA_MSSQL_ODBC_DRIVER, you can specify which ODBC driver to use to connect to the SQL Server. Possible values arelibmsodbcsqland libtdsodbc.- If
MEGALADATA_MSSQL_ODBC_DRIVERis not set, the driver is selected automatically (MSODBCSQLis the priority). - If the variable is set but the value is not recognized, a warning is logged and the driver is selected automatically.
- If
Known restrictions when working through ODBC:
- The Lock timeout is not supported automatically. You can set it manually in the Database import script:
SET LOCK_TIMEOUT timeout_period. - The
sql_varianttype is not supported. - For
MSODBCSQL:- You can't connect to old servers without changing the security settings of OpenSSL (enabling protocols and algorithms recognized as unsafe).
- If
unixODBCis compiled withoutDEFAULT_ICONV_ENCODING UTF-16, requests using Unicode characters with codes above 65535 in will not be executed.
- For
FreeTDS:- The Do not check server certificate connection option is not supported.
- If Encrypt the protocol is disabled, the packet containing the login and password is not encrypted.
- If the connection is lost it is not automatically re-established.
For MS SQL, support for the xml type when connecting via ODBC is added.
Within the same connection, you can now import strings with different codepages. The Codepage parameter in the connection config wizard is renamed to Message language.
Connecting extensions for SQLite
SQLite extensions are additional software components that add new features to the standard SQLite kernel. Many useful extensions can be found on specialized resources (e.g., https://github.com/nalgeon/sqlean or https://sqlpkg.org/).
To use these extensions, you must download and save them into the sqlite folder located next to the Megaladata executable file:
- Windows default path:
C:\Program Files\Megaladata\Server - Linux default path:
/var/opt/megaladata/server
Important: Be careful choosing extensions. Those that work with files have direct access to the file system bypassing Megaladata file storage.
Other changes in working with databases
In the Database export component, you can now completely re-create tables. In the node configuration wizard, the modal window for table creation now has the setting Delete existing table. If it is enabled, running the node includes two steps:
- Removing the existing table (if it exists) using
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table_name(or the equivalent command for DBMSs that do not supportIF EXISTS). - Creating a new table through a relevant SQL query.
When the Delete existing table option is enabled, an additional read-only text block displaying the deletion command appears on the SQL query tab above the main table-creating query editor. For ODBC connections and MS Access, the delete query is performed in error-ignore mode.
Additionally, the Database export component now supports creating columns with the maximum possible size (mapping to types like nvarchar(max), ntext, or clob). The table creation dialogue offers a specific String(max) data type, as well as an All string(max) button, to convert all string fields at once.
When exporting to a database, you can now set key fields during table creation. The table creating dialogue in the Database export node wizard now includes options for selecting key fields and enabling a Not NULL parameter. Batch editing of fields is also supported.
In the Database import node's wizard, the Choose table mode now displays table field descriptions. (Note: This is not supported for SQLite and Excel connections.) Additionally, a Generate field captions from descriptions option has been added. When enabled, field captions, including those in the preview and filter settings, are populated from the database field descriptions. If a description is missing, the caption defaults to the field name. This setting is visible only if the database supports field descriptions.
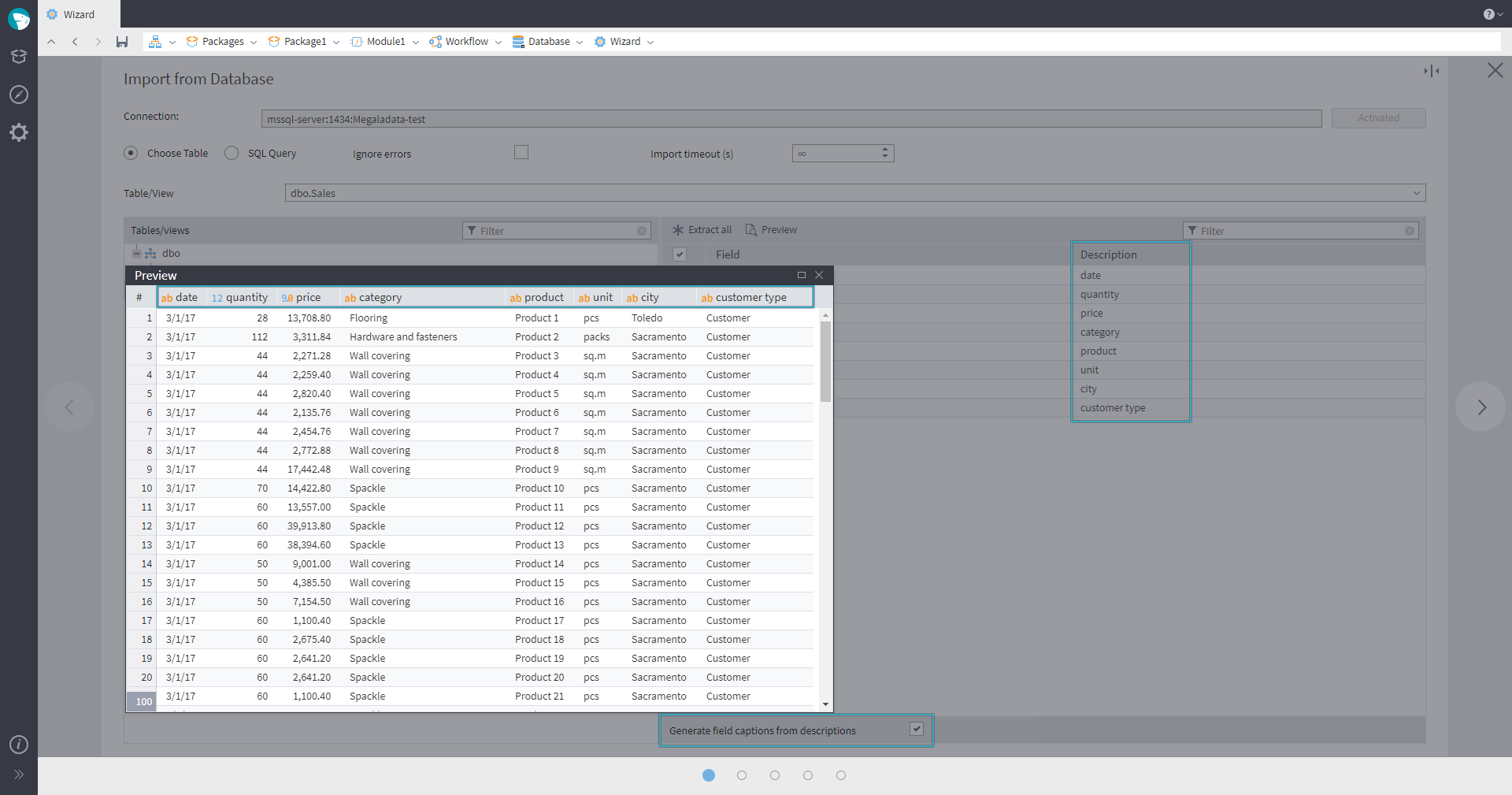
Generating field captions from descriptions
In the Preview pane of the Database import node, it is now possible to copy data directly to the clipboard.
For MySQL, PostgreSQL, and ClickHouse connections, a Check server certificate setting has been added to the SSL settings. This setting offers the following options:
- Off: The certificate is not checked.
- Signature only: Only the Certificate Authority (CA) signature is checked (not available for ClickHouse).
- Full: Both the CA signature and the host are checked. This is the default option.
This allows you to configure verification using system certificates. To do this, leave the CA certificate parameter empty.
Note: If the Always verify all certificates option is enabled in the MGD security settings, the Full check mode is enforced. In this state, editor fields become read-only, preventing manual certificate specification, and any previously entered values are ignored during execution.
For packages prepared in earlier MGD versions, if no CA certificate was specified, verification remains disabled. If a CA certificate was set, the Signature only mode is used for MySQL and PostgreSQL, and Full mode is used for ClickHouse.
When exporting to PostgreSQL, the modes—Append data to table, Clear table and append data, and Execute TRUNCATE and refill with data—now provide a Use fast loader setting with the following values:
- Auto (default): The system automatically decides whether to use the fast loader. It will not use the fast loader for views (
VIEW,MATERIALIZED VIEW), rule tables (RULE), or unsupported field types. If the system detects these conditions, it reverts to the standardINSERTmethod. - Yes: Forces the use of the fast loader (using
COPY BINARY ... FROM STDINto write rows). - No: Forces the export to use standard
INSERTrequests.
Note that for small datasets (less than 100 rows), the standard INSERT method is used regardless of this setting. When the Use fast loader option is enabled, we recommend increasing the Count of rows in a batch to improve export speed.
Note: The Auto mode is the default, even for legacy packages, which may occasionally impact performance.
Added a prompt for login/password when connecting to the data store in interactive mode.
A configured connection can now be cloned.
Added support for Oracle Database 23. For OCI 23 and above clients, the BOOLEAN fields are now detected as Logical.
For MySQL, libmysqllicient 24 is now supported (when running Linux). Corresponds to MySQL Server 9.0.
Megaladata no longer supports Interbase connections. In existing packages, configured Interbase connections will be automatically replaced with Firebird.
Changes in working with web services
Important: In the REST Service and SOAP Service connections, the Data exchange timeout (ms) option has been removed. When obtaining data, all network transactions, except for establishing the connection itself, now work without timeouts. In all packages created in the earlier versions of Megaladata, this parameter also won't be displayed.
The Overall timeout (s) property has been added to the REST Request and SOAP Request wizards, replacing the previous data exchange timeout. Allowed values range from 0 to 2073600 (24 days). If the timeout is reached, an error is sent to the output port and processing terminates. By default, the timeout is unlimited (∞).
In the configuration wizards for REST Service and SOAP Service connections, the parameter Ignore SSL certificate errors has been renamed to Do not check server certificate. If the Megaladata security settings Always check all certificates or Always check HTTPS certificates are enabled, this parameter is hidden from the wizards and ignored during node execution.
When you configure the REST Service or SOAP Service connections, you can explicitly set the Basic authentication type. In this case, the first HTTP request sends the title Authorization: Basic base64(<username>:<password>). If the server's response is 401 Unauthorized, no attempts to use other authentication types are made.
Added support for NTLM and Negotiate authentication types for HTTP requests. Negotiate only works through NTLM, i.e. without Kerberos support. For the NTLM protocol, only the V2 version is supported .
When configuring a REST Service connection, you can now set the URL parameters type:
- Query string: The parameters are included in the query string as
param-name=param-value(as before). - Add segments: This method appends parameters directly to the query path. E.g., if the base URL is
http://example.com/operation-path, running the REST Request node appends the parameter values in order:http://example.com/operation-path/value1/value2/....
Important:The node preserves the order of the parameters as they appear in the table. Since the URL structure is order-sensitive, changing the sequence in the table will change the query result.
- Replace: The parameters can be added to the URL line using special
:param1syntax. In this case, you cannot add parameters in the table.
REST Service connection parameters are defined exclusively during the initial wizard configuration. If the URL is changed dynamically via a variable, the parameters are not updated; the original names, types, and list of parameters remain in effect.
Empty parameter names are no longer supported for any type of URL parameter.
For the REST requests POST, PUT, and PATCH, you can also add URL parameters now.
In the settings of the REST Request node, new parameters have appeared:
- Wait between requests (ms)
- Repeat requests after an error
- Wait after failed request (ms)
These settings allow you to handle errors related to rate limiting (excessive requests per time unit) or server overload. Retries are triggered in the following situations:
- A network error
- The server returned
408(Request timeout) - The server returned
429(Too many requests) - The server returned any of the
5xxerrors
If the request results in an error, an entry is added to the log. During subsequent retry attempts, failures are logged as warnings (warn) rather than errors. A full error is logged only if the final attempt fails.
New features of working with Python
You can now set up a Python environment (the name of basic container image) through the Python component parameters and node settings. New settings have been added to the component's parameters:
- Default environment (PY_ENV): Passes the
PY_ENVvariable to thepython_run.shscript to launch a specific isolated environment.- Value: Selected from Known environments or entered manually (if Allow unknown environments is
true). - Defaults:
python(Linux);unspecified(Windows).
- Value: Selected from Known environments or entered manually (if Allow unknown environments is
- Known environments: A predefined list of environments available for selection in the Python node. This list is maintained by the administrator to match the server's Python configuration.
- Allow unknown environments: Controls whether users can enter environment names not listed in Known environments.
- If
false(default on server editions): Strict validation is active. The node will fail if configured with an environment other thanPY_ENVor those in the Known environments list.
- If
- Use PY_ENV as (Linux only): Defines the isolation strategy. Passed to
python_run.shvia thePY_ENV_USAGEvariable. The predefined values are:venv: Treated as a path to a virtual Python environment.image: Treated as a docker image name (one environment per image).
- Container CLI (Linux only): Specifies the containerization tool.
- Condition: Available only when Use PY_ENV as is set to
image. - Variable: Passed to
python_run.shviaDOCKER_OR_PODMAN. - Values:
dockerorpodman.
- Condition: Available only when Use PY_ENV as is set to
Important: Environment parameters are passed to python_run.sh only if the Pass node environment variables option is enabled (true ).
We've added the parameter Environment variable PY_ENV to the Python node config wizard: It is displayed if the Pass node environment variables setting is true and Python is running in a separate process. The parameter value is set through a drop-down list, which contains the following elements:
- Default: The value set in the Default environment (PY_ENV) component parameter (
PY_ENV) is used. - Values from the Known environments list. If the Allow unknown environments component parameter is disabled, you can only select the value from the list, otherwise you can specify your own value.
For the Interpreter path option, the predefined value python_run.sh has been added to the Linux parameters.
The Python node has a Control variables port added. Through the control variable value, you can dynamically select the Python environment and set the value of the Start wait timeout (ms) option.
In the Python node, it is now possible to add an arbitrary number of output sets. If there is more than one output set, the output column setting page of the wizard changes so that each output table is configured on a separate tab.
Changes to JavaScript and JS Fetch API
Updates to the JavaScript component:
Multiple output datasets: The component now supports a customizable number of output datasets. When multiple datasets are used, the wizard organizes column settings into separate tabs for each output table.
Updates to JS Fetch API:
- SSL verification: HTTPS server certificates are now validated by default (previously disabled).
- Credentials: Added support for requests containing HTTP authentication credentials (username/password).
- Timeouts: Added the
AbortControllerclass to enable timeout configuration for Fetch API REST requests.
New functions and preview in calculators
In the Calculator, new functions for determining the number of full time intervals between the dates were added:
QuartersBetween (Date1, Date2[, Absolute_Value = True]): Returns the total number of quarters between two dates.WeeksBetween (Date1, Date2[, Absolute_Value = True]): Returns the total number of weeks between two dates.
If Absolute_Value = False and Date2 is earlier than Date1, these functions will return a negative number of time intervals between the dates.
We have also added some functions of the SHA-2 cryptographic family: SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, SHA512_224, and SHA512_256.
A debug console, similar to the one in JavaScript nodes, has been added to the Preview window for Calculator (Table), Calculator (Variables), and Calculator (Tree).
If an error occurs in expression mode, the console displays the error description and a call stack. The stack is formatted as a comma-separated string of functions and operators, tracing the error from its origin up to the initial call. This trace is also recorded at the debug logging level.
In the descriptions of the Calculator functions, Khi2 is replaced by Chi2. The function names DKhi2, FKhi2, PKhi2, and InvKhi2 remain for backward compatibility, i.e. both variants of these functions are available by name, but only new names are available in the description.
New features when importing data from file sources
Multiple import of text and Excel files can now be executed in parallel processing mode, which speeds up the import process. The corresponding parameters are added to the wizards of these nodes.
We have enhanced text and Excel imports with a new Autodetect columns option. This functionality works similarly to a database select query, allowing you to automatically determine parameters for All columns or New columns only. By enabling Autodetect columns, the node dynamically adapts to structural changes. If a source file arrives with extra columns, the node processes them automatically without needing manual reconfiguration
In XML File import nodes, a customizable property Validate against Schematron has been added. If the option is enabled, the Schematron verification of the rules described in the XSD schema is performed when importing.
Changes to other components and connections
Row Filter: You can now define a list of filter values using a control variable. This feature is supported for fields with integer and string data types.
In Grouping and Table to Variables nodes:
- New separators: Added support for New line Windows (CRLF), New line Linux (LF), and Tabulation (⭾) in the List aggregation option.
In the Imputation component:
- New method: Added Replace with the previous value. This fills data gaps using the preceding non-empty value and supports all data types.
In the Join, Union, and Enrich Data components, the list of required output fields has changed. Previously, all fields in the output sets were required, but now only the following:
- In Join: All fields in the output dataset have become optional.
- In Union and Enrich Data: All fields except for the fields connecting the input datasets are not required.
In Join, we also added the possibility of joining data using a case-independent comparison of keys. By default, a case-sensitive comparison is performed, which keeps to the previously implemented logic. In order for the keys to be compared case-independently, you need to disable the Case-sensitive option in the configuration wizard of the node.
In the Sort node, sorting is now carried out in parallel via several threads. For different use cases, the node processes data from 2 to 7 times faster.
Also, a configurable parameter Maximum thread count, which has a default value Autodetect, was added. Autodetection works as follows:
- If the input data is cached from previous nodes (e.g., Field Features) or the Cache all data option is enabled, the number of threads equals the number of logical processors.
- Otherwise, the number of threads is
1, and a single-thread sorting will be performed.
For optimal operation of the node, we recommended enabling Autodetect for the Maximum thread count parameter.
In components for working with data trees, the root node can now be optional (previously, the root node has always been required, even if it was not necessary). It is important to note that:
- All nodes in the tree need to be optional, because if some node is required, then the entire chain of parent nodes, including the root, is considered required.
- None of the tree nodes should be reconfigured by the user.
Here are the conditions of the root node to be optional in different components, provided that none of the tree nodes has been reconfigured by the user:
- In supernodes : always
- Tree to Table : in the config wizard, no node is selected
- Tree to JSON: always
- Calculator (Tree): no expressions are set
- Union (Tree): always
- Join (Tree): in the configuration wizard, the node of the main tree to which the join is performed is not selected.
In Field Features, the excluded fields are now considered optional. Previously, fields marked as excluded were required. If such a field was absent in the previous node, then activating the node would result in the "Input data source" port not configured error. Such behavior contradicted the logic of excluding unnecessary fields from further processing. In the new version, if the user indicates that the field is excluded, it is not deleted during mapping, but rather, displayed in the input port wizard as Excluded.
The application now provides the ability to copy/paste variables from one port/node to another.
In the Kafka connection, hostname check is now enabled in the server certificate (ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=https). When the Always check all certificates option is enabled in the MGD security settings, it is impossible to redefine the following values: enable.ssl.certificate.verification, ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm (check of the host), ssl.ca.certificate.stores, ssl.ca.location, and ssl.ca.pem.
The XSD Schema Set connection wizard is now a single page.
New opportunities when working with visualizers
Visualizers can now be transferred from one node to another. Commands Cut, Copy , and Paste were added to the toolbar of the configured visualizers page.
In the Table visualizer, when you select the Listed/Not listed filters, you can now get a list of unique values for the column. (Previously, this functionality was not implemented in this visualizer.)
Updated mapping of tree fields and nodes
In the wizard, we added the ability to exclude fields. In the input field list, use the Add to excluded command (the field should not be a required input or lost). A similar button appeared in the output field list. Use it to add an output field to Excluded list, if the field is not associated with an input field. If the output field is associated with an input field, the command Add to excluded will add both the output field and the associated input field to excluded. Note that it is impossible to add a required or lost input field to the list of excluded fields.
The excluded elements in the list are highlighted in a separate group Excluded. They can be removed and moved. When selecting an excluded field, the input field corresponding to it is highlighted. When performing Auto link , no input fields corresponding to the list of excluded fields will be linked.
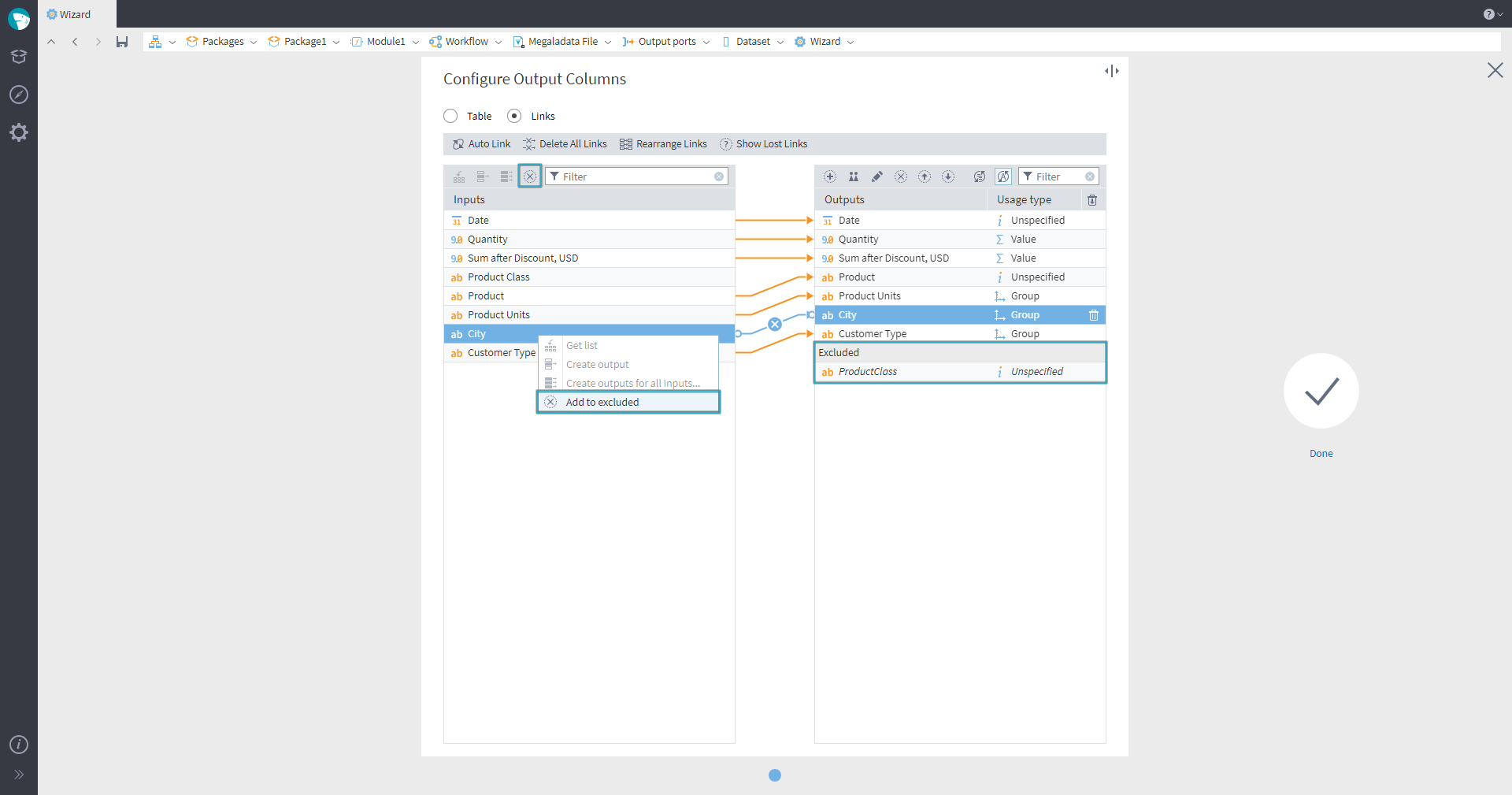
Mapping in Megaladata
In the data tree mapping wizards, the ability to exclude nodes has been added. In the list of excluded nodes, you can add a non-connected input node using the context menu command Add to excluded. In the output tree, you can add an Excluded subnode using the Show excluded switch. If there are already some items in the excluded list, you can delete or close this subnode.
Excluded tree elements are highlighted in italics. They can be removed or moved. When selecting an excluded node, the input node corresponding to the full path of the excluded node is highlighted. When performing the Auto link action, the input nodes satisfying the list of excluded are not linked.
Required fields in import nodes
Determining required fields in import nodes: If you select specific fields (e.g., by checking them), they are treated as required outputs of import nodes. These fields must be mapped to input fields, and cannot be excluded in mapping wizards when setting up output ports.
The table describes the required and optional fields for the components responsible for the import of data:
| Component | Required fields | Optional fields |
|---|---|---|
| Database import | In Table mode, all fields selected for import in checkboxes | In any other case (e.g., import by * or via SQL queries) |
| Text File import | All fields with the Use attribute assigned by the user in the Configure import formats wizard page | All other cases (All fields in Autodetect columns: All mode; all new fields in Autodetect columns: New only mode) |
| Excel File import | All fields with the Use attribute assigned by the user in the Configure fields wizard page | All other cases (All fields in Autodetect columns: All mode; all new fields in Autodetect columns: New only mode) |
| XML File import | Fields explicitly selected by the user to be included in the output dataset | |
| XML Parsing | Fields explicitly selected by the user to be included in the output dataset | |
| SOAP Request | Fields explicitly selected by the user to be included in the output dataset |
In the packages created in earlier MGD versions, all columns in all file import, XML Parsing and SOAP Request nodes will remain optional (old logic is maintained).
New administration opportunities
Password policy
A new group of settings, Password policy settings, has been added to the administration section of MGD Enterprise. These settings define the minimum requirements for local account passwords and are stored in the Settings.cfg file.
There are five predefined policy profiles with varying requirements, as well as a customizable user profile.
Regardless of the selected policy, the maximum password length is limited to 1024 characters. Additionally, the existing restriction remains: passwords cannot begin or end with a space.
Please note that password policy restrictions do not apply to existing passwords.
Security parameters
In the security parameters, an option to enforce global SSL certificate verification during the TLS connection stage has been added. This parameter affects file imports by URL, the JavaScript component (Fetch API), LDAP and OpenID authentication, and the following connections:
- REST-service
- SOAP service
- Kafka
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- ClickHouse
A similar setting Always check HTTPS certificates includes a forced verification of the server certificate for HTTPS connections and affects the operation of import from file sources by URL, the JavaScript component (Fetch API), OpenID authentication, and connections to web services.
Added settings to limit concurrent sessions (simultaneous connections using the same account from different locations):
- Disable user multisessions: Prevents a user from logging in if there is already an active session for that account (disabled by default).
- Restrict multisessions for admins: Configures behavior for Administrator accounts when multiple sessions are attempted. There are three options:
- No: Administrators can log in with the same account from multiple locations simultaneously (default).
- Deny login: Prevents the login if an active session already exists for the account. This mode is not recommended. If used, ensure that Session disconnection timeout and Connection check period are enabled to prevent stale sessions from permanently locking out administrators.
- Close current sessions: Closes any active sessions for the account before processing the new login. If the existing session cannot be closed, the new login is denied.
When working on Windows, the optional use of OpenSSL instead of SChannel is added to HTTPS requests. To use it, set a true value for the security parameter OpenSSL has higher priority than SChannel for HTTPS. The parameter applies to the REST Service and SOAP Service components. The option can solve the SSL/TLS error problem when performing requests to external systems with activated SSL certificate check.
Important: Added a check for the domain name or server IP address to which the certificate is issued. In the packages prepared in the previous versions of Megaladata on Linux, it may cause REST Service and SOAP Service HTTPS connections to fail without the option Do not check server certificate or when using a client certificate from a file. Kafka connections via SSL may be affected similarly. If this occurs, the connections will need to be reconfigured.
Connection parameters
For Unix socket connections, a new Unix socket permissions option is available. This option defines which users are authorized to use the socket, thereby securing the data exchange between processes.
The parameter value is specified in octal notation. The default value is 770. MGD Server and MGD Integrator run as different users but share a common main group, which is used for communication via the Unix socket file.
Since Unix sockets only require write permission, it is unnecessary to grant or deny read or execute permissions. Therefore, the value 770 actually operates like 220 .
This parameter is only available if MGD Server is running on Linux. If the value is changed, the server must be restarted for changes to take effect.
OpenID and LDAP parameters
The Response format option used to generate an authentication request via OpenID and analyze the response after successful authentication is added to OpenID settings. The parameter can have one of two values:
- Query parameters: The response parameters from the OpenID provider are located after the sign
?in the address bar. - Fragment parameters: The response parameters are located after
#(used by default).
The option allows you to configure authentication through Google. Please note that their tokens are not JWT, so no information other than the username is obtainable in this case.
You can check the LDAP and OpenID settings in the LDAP Parameters and OpenID Parameters, respectively, clicking Test in the Authentication testing setting.
When testing LDAP authentication, filling the following parameters is checked: Host, Account, Password, Basic domain name, LDAP filter, and Attribute with username.
Information about the test connection is displayed in a separate window. In the same window, you can perform a test search for a user.
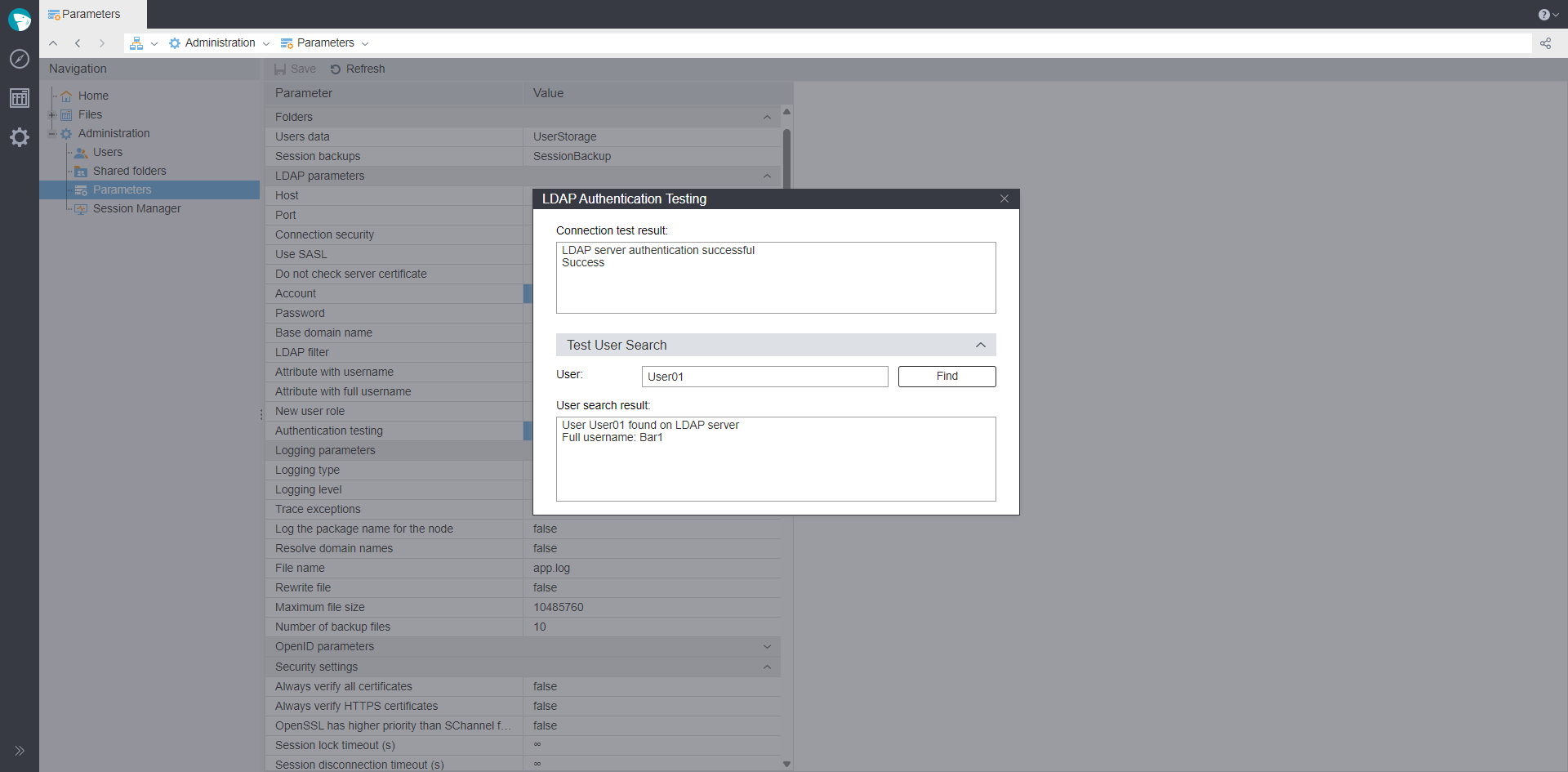
LDAP
When testing OpenID, a new browser page opens, directing you to the external authentication provider. Upon successful authentication, this page automatically closes, and a new window appears displaying the OpenID test results. These results detail all stages of the authentication process, from the code-token exchange to the retrieval of custom claim values.
We have added a Do not check server certificate settings in the LDAP and OpenID settings. Now, the server certificate is validated by default (because of this, LDAP and OpenID authentication may stop working). If the check is not needed, turn it off by enabling the above parameter.
Logging settings
In the logging parameters, the Log file deletion option is added (available in server editions). If the parameter value is true, the information about deleting files or directories from the File Storage is recorded in the log.
Additionally, logging for the number of rows in the output table port upon node activation has been added. Information about the number of records is written to the node log if the Log row count option is enabled in the node settings, or if Log row count upon node activation is set to true.
Users page
In the user account settings, a new setting Allow saving DB password has been added. The option is available only for the Workflow design role. It is taken into account when configuring a database connection. If the checkbox is enabled, the value of the Login prompt parameter will be automatically set to true when you open the connection configuration wizard, and will become ineditable. The checkbox does not affect previously configured connections. The Login prompt checkbox is automatically set only when the connection settings wizard is opened. The value of this parameter can be obtained from the OpenID token.
When updating Megaladata to version 7.3 (with the Users.cfg file created in earlier versions), the rights to save passwords for connections are granted to all users with the Workflow design role. If there is no Users.cfg file when you run the server, the default user ('user') is given the rights to save DB connection passwords.
The Megaladata administrator can now require the user to change their password. In the user editor window, the Require password change on next login option has been added. If the checkbox is enabled, the user will receive a pop-up window requesting a password change at the next login. After the user changes the password, the option is automatically deactivated and the request will not appear again. Information about password changes and unsuccessful attempts is recorded in the log.
Important: If this option is enabled for a user who does not have the right to work interactively, the user account will be impossible to use. For example, if a service user has Require password change on next login enabled, an Integrator call will result in an error: "User password must be changed" (provided that the Integrator doesn't have free MGD Server sessions cached).
On the Users page, we added search capabilities for the Username and Full name columns:
- The Search button was added to the toolbar to open the search form.
- In the drop-down menu of these columns, a search bar is now available.
Shared folders
The name of a shared folder can not contain characters: \ / : * ? " < > |.
Job scheduler
The Job scheduler now has additional triggers to start jobs:
- Run after completion of another job: Allows you to configure the job to start after a successful or unsuccessful execution of another job, several jobs, or the same job.
- Run on server launch: The reference point to run the package is the moment the server launches.
The Add job window now has a new tab: Triggers. The Scheduler tab has been moved and is now located within this new tab.
Jobs in the Scheduler now have a Maximum execution time parameter, which is available if the Limit execution time checkbox is marked. The Maximum execution time value can be set in seconds, minutes, hours, or days.
When creating a schedule in the Scheduler, you can now specify not only the days of the week or month, but also the start time and duration (for example, run the package from 9:00 every hour for 8 hours). It is also possible to combine days of the week and days of the month when setting up the job launch schedule.
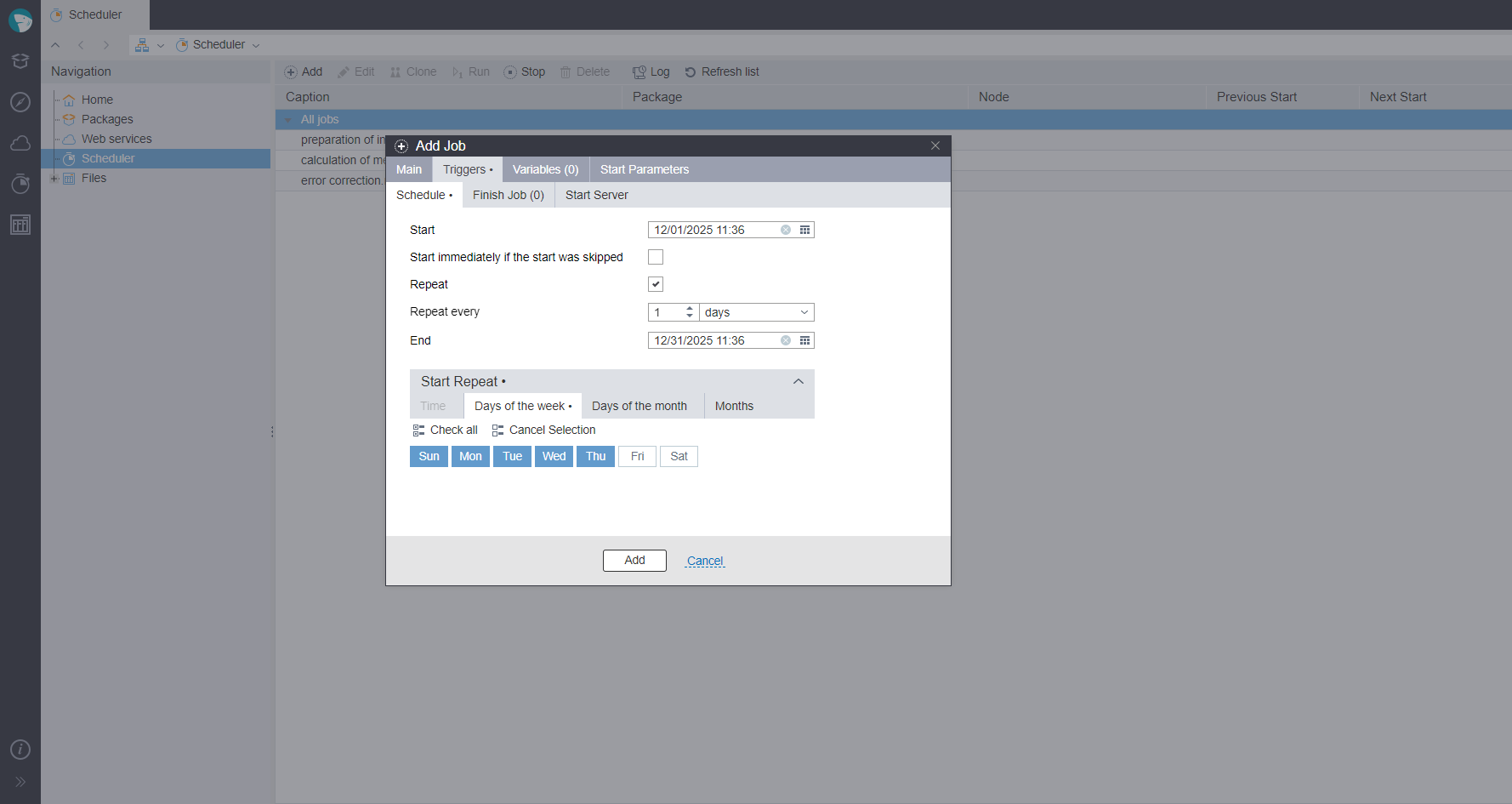
Job Scheduler
In the Variables tab of the job settings window, a Select from package option has been added. It allows you to select all or several variables from the package to add to the list of job variables. This feature is especially convenient when there are many variables in the package or the supernode.
In the Scheduler log, we added the ability to view detailed error information. When clicking on the error text in the table of completed sessions, a window with detailed description opens.
BatchLauncher
In BatchLauncher, the ability to connect to the MGD Server via a Unix domain socket has been added. The Unix domain socket file name is indicated via the port parameter. The Unix domain socket is considered set in the parameter if it has a value other than a port number (ranging from 1 to 65535) or if the address parameter is not set.
A new start parameter, -deactivate, has been added. It controls the sequential deactivation of node groups after they are fully executed, to release memory used by the workflow. Setting -deactivate=false disables automatic deactivation (even when enabled in package/server settings), and -deactivate=true enables it. Using the option without a value (i.e., -deactivate) acts as -deactivate=true.
Important: Previously, the -deactivate key was interpreted as transmitting a variable named deactivate to the currently running package. Now, this key controls the automatic deactivation of nodes. If you need to set the deactivate variable value, use the following keys:
.deactivate=value–for a package variablePortName.deactivate=value–for a node variable located inside thePortNameport.
When BatchLauncher starts without parameters, the first output line now displays the program name and version (e.g., "Megaladata BatchLauncher version), followed by the utility command syntax. (Previously, only the syntax was displayed).
Automatic deactivation of node groups after complete execution
Parameters have been added that allow you to configure a forced chain deactivation of node groups after they are fully executed, to release the memory used by the workflow. The option can be enabled globally in the server settings, configured at the package level, set in the Job Scheduler, or passed as a BatchLauncher parameter.
Node deactivation is triggered after the node is unlocked during activation. At this point, the system checks whether the node has descendants (nodes connected to the output ports, excluding those connected via execution order ports) and whether the node is a supernode output node. If these conditions are satisfied, the process of deactivating the nodes in reverse order starts.
This process does not include nodes that have their output ports connected to other nodes, which are active or in the process of activation and not yet included in the deactivation list. This is made to avoid conflicts with node activation in parallel workflow branches. The node execution order does not affect the automatic deactivation order; that is, when a node is deactivated, all its descendants are also deactivated (except for connections through execution order ports).
Chain node deactivation operates via links, except when they refer to nodes from shared packages.
Peer authentication
In Megaladata 7.3, a new type of Peer authentication is available for Linux. This authentication method uses the operating system user's name and eliminates the need to enter a password for local connections, reducing the risk of account data interception.
Peer authentication is only available when connecting to MGD Server through a Unix socket. Specifically, this type of authentication is used for the user account under which Integrator or BatchLauncher connects to MGD Server. For users connected to the server interactively through a browser, this option is not applicable.
In the Users page in Administration, the add/edit user window now has a new System user field for the UID or username of the current system user. If System user is not specified, it is assumed that the operating system username matches the login field. The System user field is editable if the Peer type is selected in the Authentication field and the login (username) field is empty.
In the configuration files Users.cfg and Integrator.dll.config, a Peer connection is configured for the service user. Thus, with a new installation, Integrator will connect to MGD Server with Peer authentication by default.
Megaladata installation on Linux
When Megaladata is installed on Linux, for users with the administration (Admin) role, the checkbox requiring a password change is enabled by default. Thus, the administrator password is changed not during installation, but at the first Admin login through the web interface. This option is especially useful for cloud installations.
When updating MGD Server installed as a service, the user version of the server.json file is now preserved. Previously, this file was replaced by the standard version from the distribution, and user settings were lost. This could lead to Megaladata failure after the update and require additional configuration.
Debian 13 (offered by default) and Astra Linux 1.8 have been added to the list of base images for Megaladata Server.
Now you can use base images not only from docker.io (as before), but also from other repositories.
Performance optimizations
Low-level optimizations have been implemented, allowing for better utilization of hardware resources.
The process for determining executed packages and nodes in the Integrator has been optimized, increasing performance in cases where a large number of Integrator queries are executed. These queries can now be processed in fractions of a second.
Parallel Loop operation has been optimized. The output dataset is now populated in parallel using multiple threads. As a result, the Loop now performs up to 5 times faster.
Expressions in the Calculator are now calculated 7%–70% faster (depending on expression complexity and functions used).
The following Calculator functions have been optimized: Replace, Trim, Upper, Lower, CRC32, MD5, and SHA1.
The creation of package node trees upon opening has been optimized. As a result, large packages now open 20% faster, with significantly reduced RAM consumption.
The tree mapping wizard now opens faster.
Optimization has affected many parts of the platform. Depending on the usage model, users will experience different increases in speed. Measurements show that the speed boost is observed both when performing simple workflows with typical data operations (import, sorting, grouping, etc.) and when processing large amounts of data in high-load systems.
When running on Windows, the speed is on average 20% higher compared to version 7.2. For Linux, the progress is even more noticeable: the new version is 28% faster.
Usability improvements
For workflow nodes and connections, you can now generate a caption automatically based on the component settings. The auto-generated caption will abbreviate the node settings. For example, for import from file sources, the automatic caption will contain a file name or variable name if the path to the file is set through a variable. For the Unpivoting node, it will be formed as: Info: + list of information column captions + Transp.: + list of transposed columns captions.
The user can manually choose the mode for generating the node caption. In packages created before version 7.3, the Custom caption mode will be available for all nodes, while the Auto-caption mode will be used by default for all nodes added to the package in version 7.3.
A copied or cloned node inherits the caption mode. If the original node caption was auto-generated, the copied/cloned nodes will not have an index added. For Node Execution Loop, and Reference nodes, the caption is generated based on the referenced node's caption.
For a Reference Node linked to a connection, the caption will change if this node is reconfigured for another connection.
The maximum number of rows for node captions is limited. Multi-line captions could completely overlap the node and elements below, blocking access, so only the first three lines are displayed for long captions.
For MGD desktop, window titles display the name of the package and the path inside the package.
Markdown syntax can now be used to format the text of annotations and comments. The Markdown syntax for annotations and comments option has been added to the package properties and is enabled by default. In annotations, you can also use images and hyperlinks. To do this, change the security settings URL for loading images and URL for generating links on the Parameters page in the Administration section.
In the derived component wizard, a new field displaying the component's GUID has been added. A similar field now appears in the visibility configuration of connections.
In the Search modal window of the Navigation pane, there is now the ability to search for workflow elements by both GUID and Mark. You can also specify the type of component by which the search will be performed: node, derived component, connection, or any. The search can be started from the selected node in the Navigation tree by enabling the Start search from selected option.
In the Cube visualizer, if you hold Alt when clicking a non-empty cross-table cell, the related data point will be highlighted in all open cube charts (if it does not belong to a hidden series). The same way, if you click on a data point in a cube chart, the related cell of the cross-table will be highlighted, and the table will scroll to it.
For package variables, user variables, and control variables, a multi-line Description field has been added. In the Calculator (Variables) node, the Description field is transmitted from the expression to the Description field of the output variable, including in Replace mode.
When cloning a node, its visualizers are transferred to the newly created node.
The Processes pane now displays the remaining time of the process.
Improved automatic node alignment in the workflow construction area.
Improved error reporting & logging
Previously, in TLS connections, if a connection error occurred that was unrelated to TLS, the message was uninformative. We have added dedicated processing for such situations so that users receive detailed error information.
Error messages when testing connections have become more informative. The user now receives specific information about the cause of the problem.
On the Login page, when connecting through OpenID takes long, a Loading indicator is displayed.
When opening a package, if linking some other package fails, the error message will indicate which package contains the failed link.
Whenever the MGD Server is stopped, a message recording this event is added to the log.
Information about the MGD version is now added to the beginning of each log file.
All errors and warnings are now displayed in a separate window, where you can also view a detailed description of the error.
The error message displays the time the error occurred (if possible).
Throughout the application, some button captions were changed from “Apply” to:
- Change: when editing
- Add: when adding something
- Save: if saving occurs at this point
- OK: in all other cases
In all deletion requests, the text of the "Yes" button is replaced by Delete.
See also



