Process Mining Development Trends


Intelligent process analysis is being rapidly implemented in a growing number of industries. To use process mining, a company needs only a minimum of data: an event log that captures the digital footprints of a process. With this information, it's possible to conduct in-depth analysis and achieve quick wins by identifying ways to optimize processes without significant additional investment in financial or labor resources.
The low barrier to entry, combined with significant potential benefits, makes process mining an extremely attractive technology. Major market analysts support this, forecasting the global process mining market to grow exponentially. Some projections show it will surpass $10 billion by 2028, driven by strong adoption in North America and Europe.
However, process mining is no longer just a standalone tool for analysis. It is evolving into the core of comprehensive Process Intelligence platforms, which combine process discovery, AI-driven diagnostics, and automation into a single, continuous improvement engine. Let's explore the key trends driving this transformation.
Main trends in the development of Process Mining
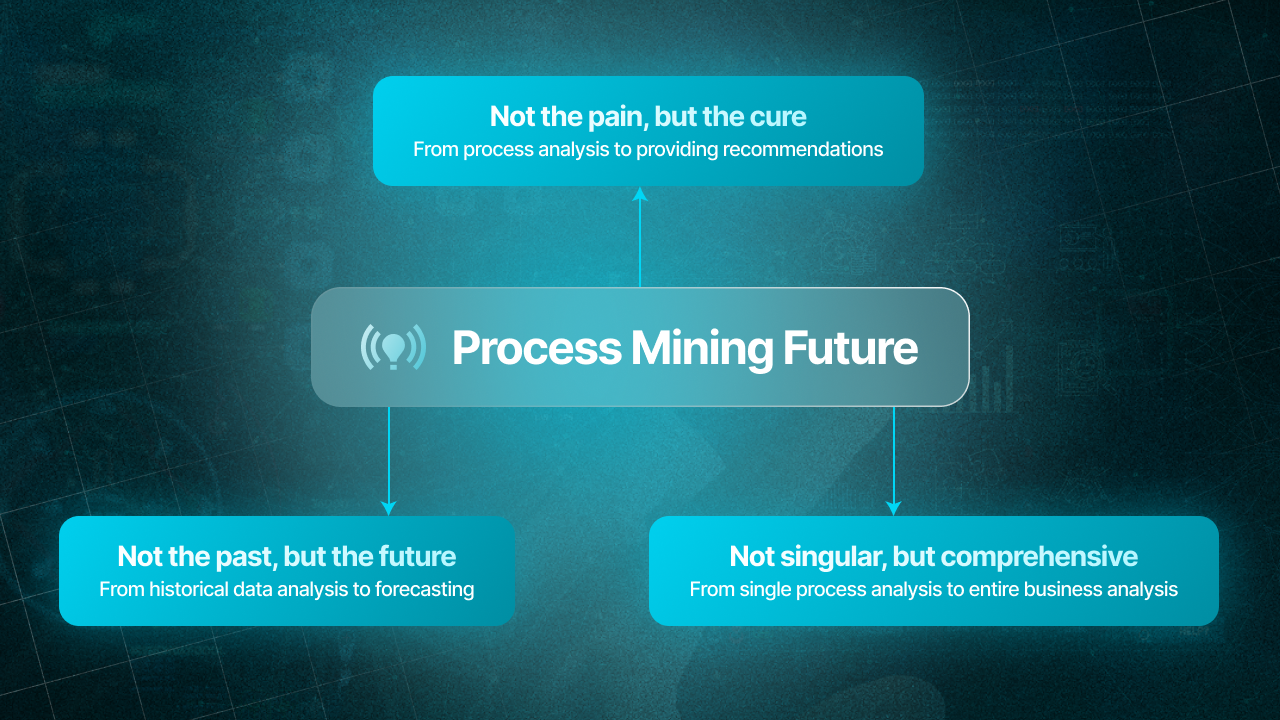
Key trends in process mining developement
From retrospective to prediction
Initially, process mining focused on analyzing historical data to identify performance problems or regulatory compliance issues. As the field has developed, new demands have emerged. Process analytics must now enable rapid reactions to process changes and, ideally, anticipate them.
This has led to the emergence of predictive process mining, which uses forecasting, simulation modeling, and machine learning. "What-if" analysis is now a critical capability, allowing businesses to test the impact of changes before implementation.
In the manufacturing sector, process mining is essential for creating digital twins (computer models of real production processes) and digital advisors (mathematical models that provide real-time recommendations for equipment operation).
From diagnostics to AI-powered recommendations
The goal of process mining is not just to analyze a process but to radically improve it. This evolution from diagnostics to "treatment" is now being supercharged by Generative AI.
Modern process mining platforms are embedding Large Language Models (LLMs), allowing users to interact with complex data using natural language. Instead of building complex queries, an analyst can simply ask, "What is the root cause of late deliveries in Q3?" or "Show me all orders that skipped the mandatory approval step."
AI makes these insights available to everyone, not just experts. It can automatically generate process improvement suggestions and even trigger automations through technologies like RPA (Robotic Process Automation). This transforms process analysis from a manual, expert-driven task into an intuitive, AI-assisted conversation.
From individual processes to holistic, object-centric view
Process analytics was first applied to standard business processes like Order to Cash and Procure-to-Pay. Its scope later expanded to non-monetary flows like Opportunity to Order, Issue to Resolution, and Sustain and Retain.
However, these processes don't exist in a vacuum. The next frontier is object-centric process mining (OCPM). While traditional process mining follows a single "case" (like an order), OCPM provides a much richer, 3D view by modeling the complex interactions between multiple business objects—such as customers, products, shipments, and payments—all at once.
This allows organizations to see how a change in one area, like product packaging, directly impacts interconnected processes in logistics, pricing, and marketing. OCPM moves analysis from a simple, linear process map to a dynamic digital blueprint of the entire business operation.
By creating a continuous feedback loop of real-time monitoring and improvement, organizations can use process intelligence to constantly optimize performance and stay ahead of the competition.
More on process management:
See also



