Use Case: Automated Solution to Determine Current Market Prices


Before
The company relied on manual search and comparison of data and extensive use of Excel tables. The process involved the following stages:
- The Procurement department would compile a list of necessary spare parts, using the company's existing database (reference data).
- Dedicated groups of specialists would then look up the parts' current prices in various sources, searching for price lists and commercial offers.
Here is a simplified diagram of the process:
Business process before automation
Problems: The procurement managers became overloaded, forcing the company to hire and train new specialists. Because the workload was constantly growing, it had to be distributed among various subdivisions, each managing separate product/service groups. The reliance on manual processes and human memory began to hinder business operations. For instance, without a centralized system, managers had to just remember all the variations of product names. The need for automation became increasingly apparent.
Together with the company's specialists, we formulated the project's goal: Implementing an automated system to save managers from routine tasks and facilitate data-driven decision-making. Reaching it would involve the following benefits:
- Reducing manual intervention (and, consequently, its cost).
- Solving personnel issues related to workload and repetitive tasks.
- Increasing the accuracy of price updates by processing larger volumes of data (in less time).
- Launching new business processes that could use the updated price information.
Data issues
The main issue with the data was its inconsistency. The data was highly unstructured, with each store or price list using its own names or abbreviations to refer to the same product.

Examples of naming the same product in different stores
Names could appear in various languages, with mixed upper and lower case letters, formatted using different standards, etc. Sometimes, typos or special characters accidentally appeared (as in example 2).
Megaladata's automated system for advanced price analysis
Here is the model we worked out for the new, automated business process:
Automated price analysis system: model
The advantages of the new model included:
- Less manual operations
- Automated data collection
- Analyzing large data amounts
- Automated monitoring and notifications
The Price Data Loader is a Megaladata pipeline dedicated to standardizing the data format before loading the data into the system. All unstructured information from various sources is processed and included to a "uniform price list".
This uniform price list then enters the price data preparation subsystem, which performs cleaning, normalization, classification, and structuring. After that, the prepared data is saved into the main database.
Here is an example of a product listing undergoing these stages:
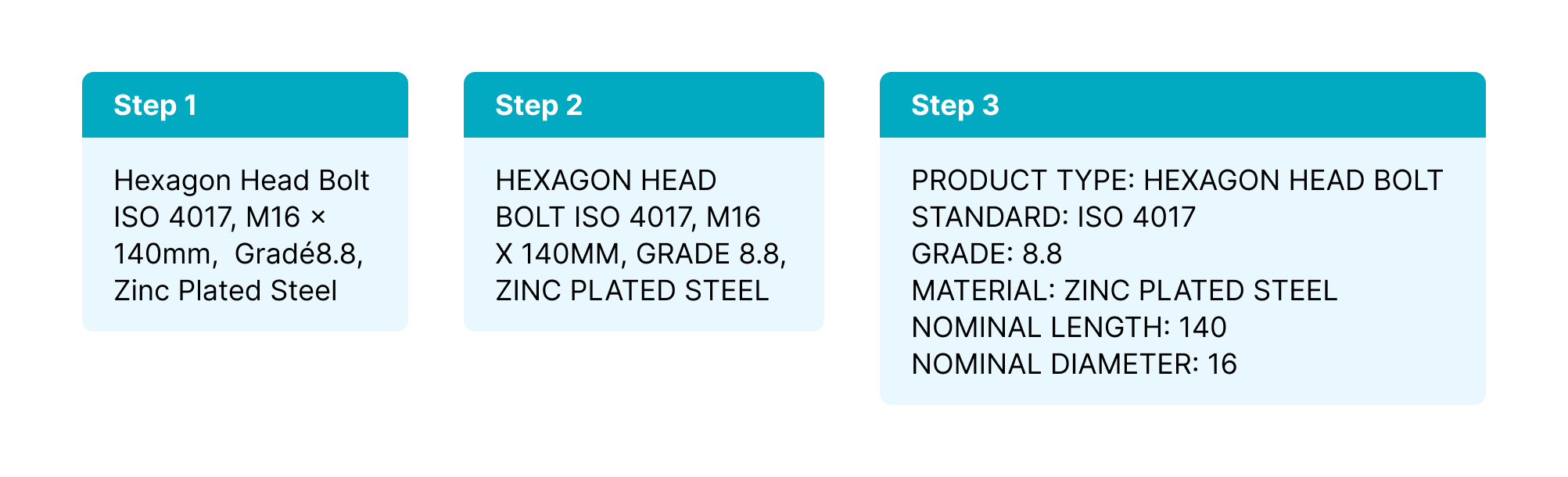
Cleaning and structuring product data
The next stage is transmitting the data to the price data use subsystem, which is a set of Megaladata workflows configured for various price calculation methods. The processing results are send to the database again. There, external users can access it from other integrated corporate systems via the integration subsystem.
Technology and structure
Analytics: Megaladata Server
- Job scheduler
- Data processing workflows
- Integration models and web services
- Back-end web services for the system's user workstations
Databases: PostgreSQL
Workstations: HTML, CSS, JavaScript
The user workstations were developed and equipped by the customer. Megaladata handles all the data processing.
The Megaladata platform allows for creating autonomous solutions, where processing pipelines do not require any manual intervention. The developed price analysis system is an example of such a solution.
Data processing flow
One of Megaladata's built-in components is a job scheduler. It allows you to start jobs by schedule, and monitors the events, logging them into a dedicated database.
All workflows follow a standard structure:
- Distributing tasks into tables
- Reading the required source data
- Running data through a processing pipeline
- Saving the results and logging
A data processing pipeline (step 3) includes the following stages:
- Data validation. Additionally, the currency, measuring units, and the product's country are determined at this stage.
- Data normalization. The data is cleaned and standardized.
- Classification—determining the ontological class.
- Determining the attributes and their values.
- Data aggregation. Performed using Megaladata's Enrich data component.
Here is how the workflow looks in Megaladata:
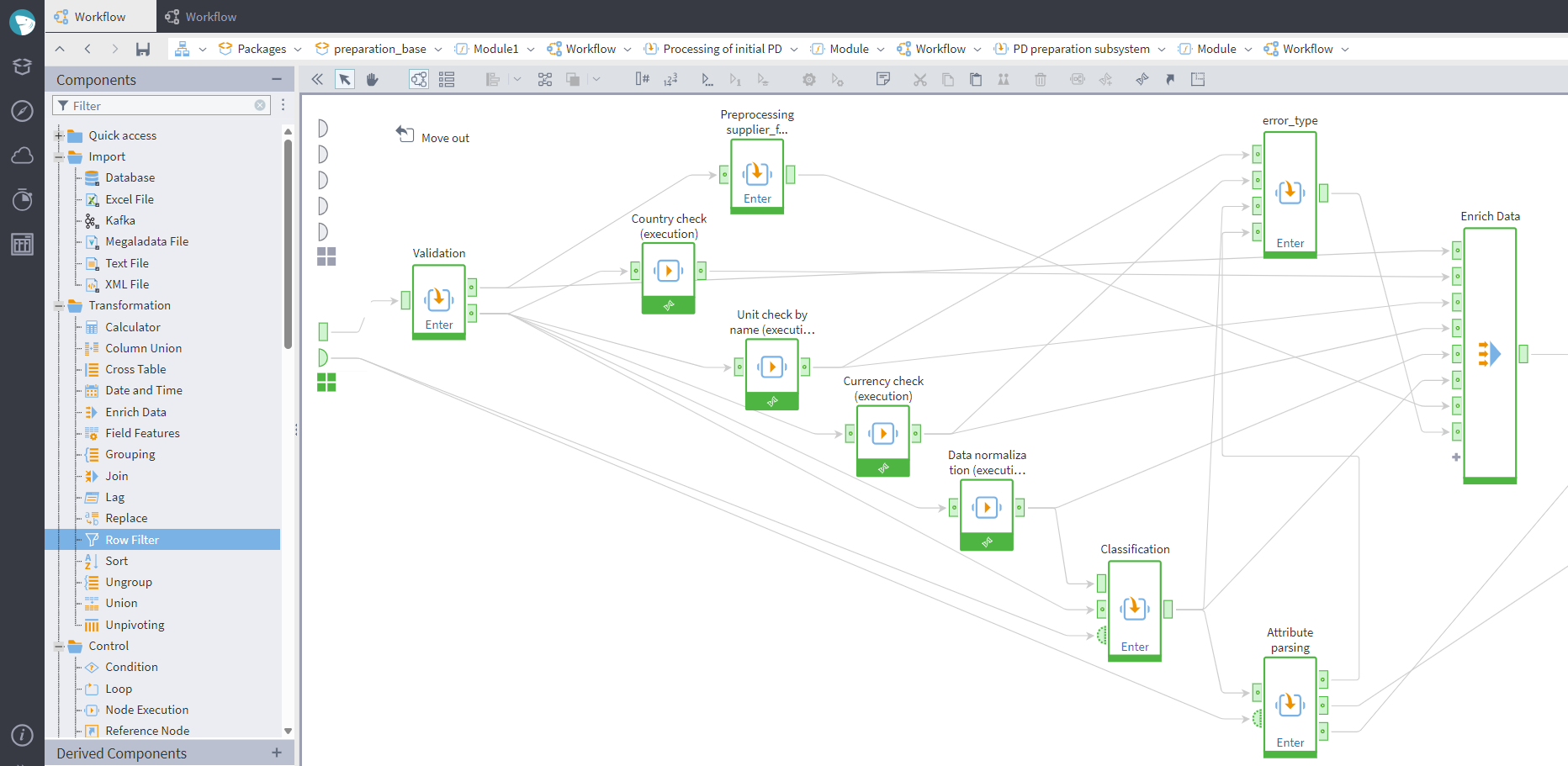
The workflow processing updated prices
Calculating prices
Price calculation involved the following steps:
- Searching for "candidates" (prices for matching products). The matching strategy between the list of products and the updated price information may be exact equality, falling within a range, or fuzzy search.
- Eliminating outliers and determining required prices.
- Selecting individual product prices for various requests.
Here is an example of a price calculation workflow:
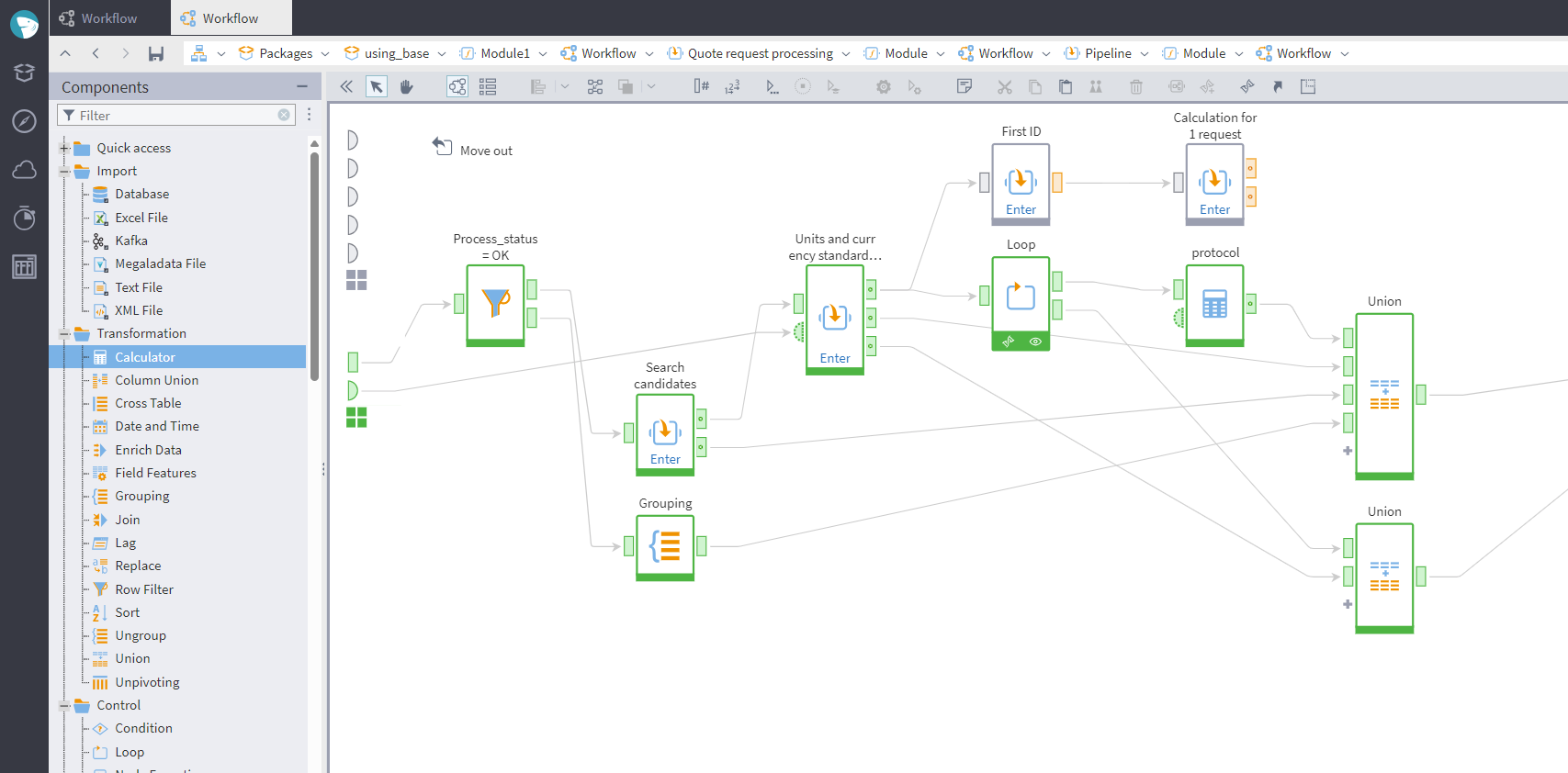
Searching for "candidates" and calculating prices
Results
The main advantage the customer gained by developing their price analysis system on the basis of Megaladata is, undoubtedly, boosting the performance. Besides, there are other advantages:
- Megaladata provides a wide range of built-in processing components and integration tools.
- You can iterate data during the development process and analyze the output of each component.
- The solution supports teamwork. You can engage field experts and analysts into working on the project.
- The system has great potential for further extension and development, thanks to being:
- adaptable: the customers' analysts can develop new price calculation algorithms and easily build them in.
- scalable: Megaladata's architecture supports both horizontal and vertical scaling.
- We offer training and support which make it easy to transfer the solution to the customer:
- Training using ready-made Megaladata workflows
- The low-code solution is easier to maintain; no need to involve programmers and other IT specialists.
- Minimal requirements for documentation: the visual workflows are illustrative on their own.
Perspectives
The developed solution—a system for updating product prices and using them in calculations—can be easily maintained and expanded by the customer. Future development could include such functionality as:
- Cleaning reference data
- Structuring other types of information for business processes
- Searching for alternative products or suppliers
- and more
A solution for cleaning and structuring data based on reference information is a key to facilitating many business processes.
See other use cases:
- dimedis: AI-driven data collection for digital marketing
- Optimizing technological processes of a steel mill
More on automation:
See also



